Last Week in ConTech - 6 October 2025
Deep Insight: Why it is so expensive to build in New York
Deep Insight: Why it is so expensive to build in New York
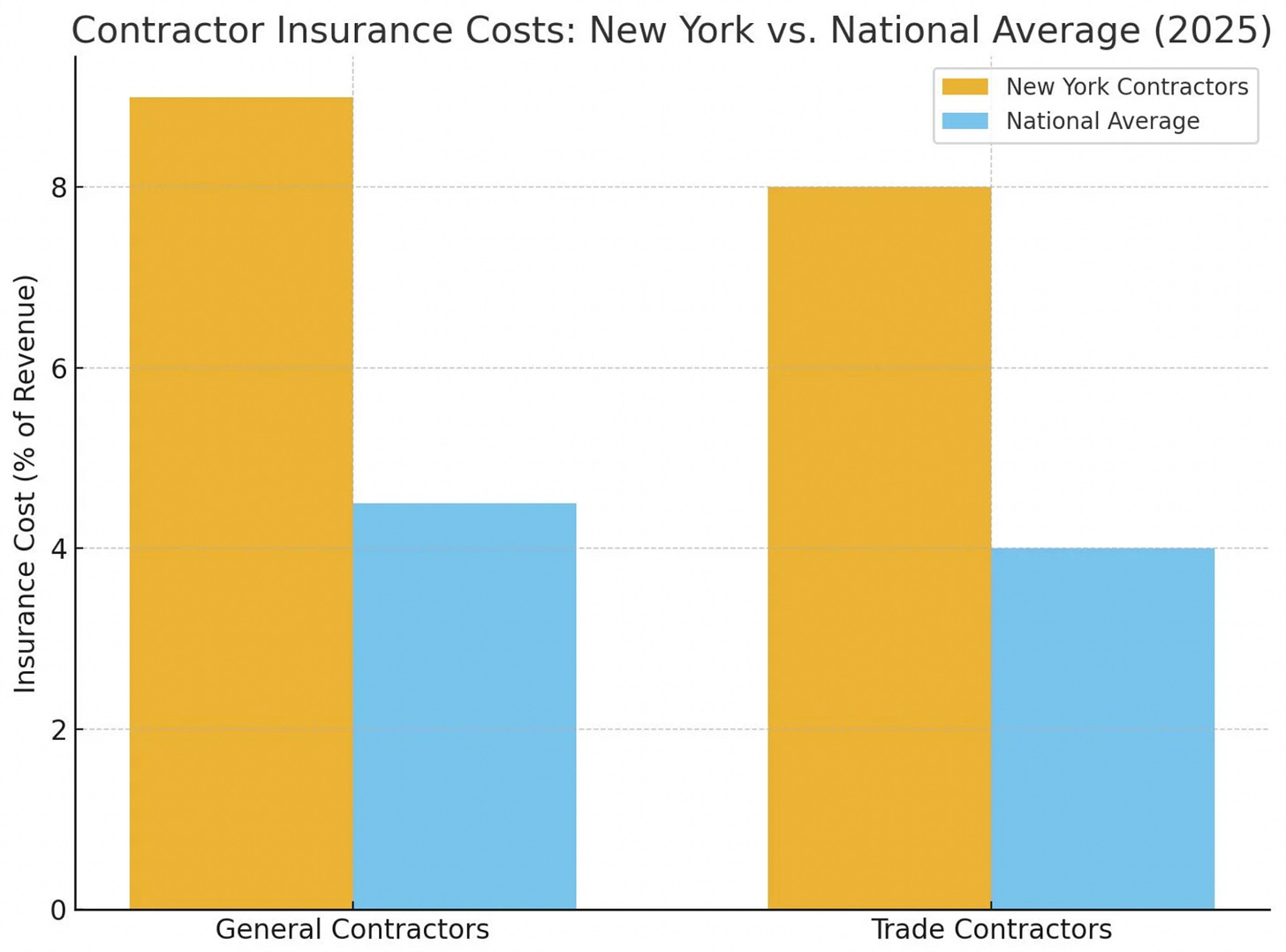
This week a contractor mentioned to me they’d never work in New York. The reason? High insurance costs.
New York is often cited as the most expensive state in the U.S. for contractor insurance, with large verdicts and settlements (averaging $4.9m per case) driving premiums upward. On average, contractors reportedly spend 7–10% of their revenue on insurance, whereas in many other states the figure is closer to 3–5%.
One major factor driving this is New York’s Scaffold Law, also known as Labor Law § 240. The law was enacted to protect construction workers performing tasks at height by requiring owners and contractors to provide proper safety devices such as scaffolds, ladders and hoists.
What makes the law particularly onerous is that it imposes absolute liability for injuries from falls or falling objects. That means if a worker proves that required safety equipment was not properly provided, maintained, or installed, the owner or contractor is liable; even if the worker was partly or wholly at fault. In effect, the worker does not need to prove negligence.
For comparison, Illinois repealed its version of a scaffold statute in 1995, replacing it with a comparative fault scheme under common law negligence. Under such systems, the injured party’s own contribution to the accident can reduce their recovery. Illinois currently uses a “modified comparative fault” rule: a plaintiff can recover damages so long as their share of fault is not more than 50%.
This illustrates how regulatory regimes intended to protect workers can impose substantial cost burdens. While safety regulation is often essential, it can also generate unintended effects such as, in this case, higher construction costs and broader social consequences through higher housing or infrastructure prices.
Regulatory reform is a wider conversation now unfolding across the U.S., where even landmark policies like National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) are being reconsidered to balance protection with progress.
In this issue there are:
12 Startup Fundings
13 Policy and Regulatory Changes
7 New National Infrastructure Projects & Priorities
0 New investment funds
1 Acquisitions
9 News articles
41 new jobs posted - view here
Reading time: 14 min
Startup Funding
Planning
Optimuse, an Austrian startup, raised €4m in funding. They are developing an AI planning platform for which interprets existing building data such as plans and schematics to create digital models and simulate decarbonization paths to optimize heating, cooling and building envelope systems quantifying the effects on CAPEX, OPEX, CO₂, and comfort. More here.
AI
Nonlinear, a San Francisco startup, raised $1.1m in Pre-Seed funding. They are building a low code automation platform for the AEC industry allowing engineers to easier create ‘building blocks’ to review, analyse or execute repetitive tasks such as QA/QC, submittal review to flag non-compliant products, estimating including quantity take offs, proposals and more. More here.
Structured AI, a San Francisco startup, raised $1m in funding. They are building AI assistants for design engineers which integrate with software such as Revit, Word, Excel, SharePoint and Outlook and automates repetitive workflows. It does so by indexing files, providing contextual assistance directly in software such as Word and syncing Review models, specs and schedules in real time and other tasks. More here.
Infrastructure Management
Cyvl.ai, a Massachusetts startup, raised $14m in Series A funding. They have developed an AI powered mapping technology which uses vehicle mounted 3D mapping sensors to help engineers inspect and manage physical infrastructure completing tasks such as detecting pavement damage, ADA issues and broken assets providing condition scores and project priorities for local governments. More here.
Procurement
Materials Mart, an Indian startup, raised ₹10 crore (~$1.1m) in seed funding. They are developing a one stop platform for construction material purchasing, offering a mobile app which allows customers to easily browse, compare and order material with doorstep delivery and bulk order discounts. More here.
Alternative site energy systems
Anode, a San Francisco startup, raised$9m in Seed funding. They are developing on demand power using battery native, mobile microgrids for the temporary power industry serving industries such as construction and live events. More here.
Notes:
Many construction sites make use of generators as there is no connection to the grid.
These are often diesel generators which are expensive and emissions polluting.
For temporary power, it is not just about delivery of the system but also the transportation and storage costs.
For example diesel has an established supply chain with standardized expectations around storage.
On the other hand with hydrogen, a challenge has been safely refueling equipment.
With diesel you can use a small jerry can but with hydrogen you often need specialized refueling equipment and formal safety protocols.
Geopura is a hydrogen focused startup working to solve this challenge for the construction industry.
Green Materials
Plantd, a North Carolina startup, raised $22m in Series B funding. They transform perennial grass into carbon negative structural building panels made for wall sheathing, roof decking and subflooring. More here.
Digital Twins
Zen Intelligence, a Japanese startup, raised ¥1.5b (~$10.1m) in Series A funding. They are developing a solution which uses a vision language model to transform 360 degree videos into 3D digital twins which are automatically mapped to the blueprints. More here.
Operations
OpusFlow, a Dutch startup, raised €3.8m in funding. They are developing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system for sustainable installation companies focusing on technology such as solar panels, heat pumps, home-batteries and electric vehicle charging stations streamlining tasks such as quotations and team scheduling to inventory management, sales operations, and invoicing. More here.
OpenSolar, a San Francisco startup, raised $20m in funding. They have developed a platform for solar installers assisting with core processes such as designing solar systems, developing customizable proposals, automating invoicing, managing hardware procurement, CRM management and more. More here.
Notes:
Google offers a Solar API as part of Google Maps which covers 400 million buildings in more than 40 countries.
Developers who hit the end point can receive information on an address such as:
A building’s location, dimensions, and solar potential including information such as roof size and slope, and modeled energy production estimates for a rooftop solar array.
Data layers including details such as shading in a location and a digital surface model of the rooftop.
Solar potential calculation determining the annual sunlight exposure on a rooftop using Google’s imagery, 3D modeling, and historical weather patterns.
I didn’t realise this data was provided natively by Google without the requirement for sophisticated algorithms on top.
It can be used to streamline top of funnel activities such as quick feasibility designs and initial cost estimates.
Building Management Systems
Viboo, a Swiss startup, raised €3.3m in Seed funding. They are developing a building management system which wirelessly connects with common IoT devices (e.g smart thermostats) learning heating patterns and controlling them proactively to reduce energy use. More here.
Inspections
ANYbotics, a Swiss startup, raised $20m in funding. They develop autonomous legged robotics for inspections of critical infrastructure facilities such as power generation or oil & gas. More here.
Other
Phaidra, a Washington startup, raised $50 in Series B funding from investors including GS Futures. They have developed a solution which uses AI agents which helps data centres optimize the electricity, liquid cooling and workload management systems and minimize energy used. More here.
Related:
Why we invested in Phaidra - GS Futures (GS Group is a South Korean energy, retail and construction conglomerate). This note is from when they invested in the last round.
Policy and Regulatory Changes
US
Energy Dept. adds ‘climate change’ and ‘emissions’ to banned words list
The Energy Department has added “climate change,” “green” and “decarbonization” to its growing “list of words to avoid.”
Other terms officials must avoid include “energy transition,” “sustainability/sustainable,” “‘clean’ or ‘dirty’ energy,” “Carbon/CO2 ‘Footprint’” and “Tax breaks/tax credits/subsidies.”
This is at its Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy.
The Office is the government’s largest investor in technologies that help reduce emissions.
Notes:
According to Wikipedia, the mission of the Office was to help transition Americans to a 100% clean energy economy no later than 2050.
It did so by investing in high risk, high value R&D.
With the removal of these terms, it is unclear how the Office’s strategy will change, likely investing in all kinds of high risk R&D across different types of energy without preferential treatment to certain types.
Government funding lapsed after the Senate rejected Democratic and Republican stopgap bills.
As part of this permitting and studies will be paused.
Notes:
The government shutdown can affect contract awards, payments and permitting for construction projects.
Trump Sets Lumber, Wood Tariffs in Bid to Boost US Industry
Trump ordered 10% tariffs on imports of softwood timber and lumber, as well as 25% levies on kitchen cabinets, vanities and upholstered wood products.
The tariffs are set to apply from Oct. 14, with some increases targeted to take effect Jan. 1.
Home builders have warned these tariffs could deter investments in new houses and renovations.
White House Freezes $18 Billion in NYC Funding as Shutdown Hits
The White House is halting $18 billion in New York infrastructure funding due to concerns over diversity and inclusion practices.
The funding freeze affects the Hudson Tunnel Project and the Second Ave Subway.
The US Department of Transportation reviewed the projects to determine if any awarded funding violated a new rule.
US Congress proposes new visa programme to ease construction workforce shortages
The Essential Workers for Economic Advancement Act (EWEA) was introduced by a Republican senator.
It would launch a new H-2C visa program designed to help industries with persistent labour gaps.
It would start with 65,000 visas in its first year, with annual levels adjustable between 45,000 and 85,000 depending on market conditions.
To protect domestic jobs, restrictions include:
Visas are only available in areas where the unemployment rate is 7.9% or less.
Employers must demonstrate that a certain position has gone unfilled for three consecutive months or is open for 60 days within a 90-day period.
Notes:
It is unclear if this bill will pass but it showcases a political desire to address construction labor shortages.
DOE ends billions in clean-energy awards after Vought post
The Energy Department said it’s terminating $7.56 billion worth of financial awards that support 223 projects funded via several of its clean-energy offices.
The funding is cut in states that all voted for Kamala Harris in 2024, have Democratic Senate delegations, and most have Democratic governors.
It includes cuts to another hydrogen hub in the Pacific Northwest set to span parts of Washington, Oregon, and Montana.
California Unveils 4000+ Companies Targeted by Sweeping Climate Disclosure Mandate
California has officially named 4,160 companies that will soon be required to comply with the state’s landmark climate disclosure laws.
This disclosure mandate is driven by two pieces of legislation: SB 253 and SB 261.
SB 253 targets companies with over $1 billion in annual revenue and requires reporting of Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions beginning in 2026.
In 2027 they must report their Scope 3 emissions.
SB 261 applies to companies earning more than $500 million, mandating public disclosures of climate-related financial risks and mitigation strategies, with the first reports due by January 1, 2026.
Notes:
This includes construction companies which meet the reporting threshold.
Proposed NY State bill would exempt Long Island construction projects from Scaffold Law
The scaffold law holds property owners and contractors responsible for all construction site falls, even in instances of worker negligence.
It holds a standard of “absolute liability,” in which property owners and employers are held financially liable for injuries caused by “gravity” regardless of fault.
Similar laws in every state except New York were repealed or amended in the 20th century.
The measure, introduced on Sept. 26 by Assemb. Ari Brown (R-Cedarhurst), would exempt projects built in Nassau and Suffolk counties from the law’s standard of “absolute liability.”
Notes:
The scaffold law is often cited as the reason for high construction insurance costs in New York.
Trump to open more federal land for coal mining, provide industry $625M to boost coal plants
The Trump administration said it will open 13 million acres of federal lands for coal mining.
It will also provide $625 million to recommission or modernize coal-fired power plants.
The tax bill approved by Republicans and signed by Trump reduces royalty rates for coal mining from 12.5% to 7%.
China
China unveils $70 billion of financing tools to bolster investment
China will deploy policy-based financial tools to the value of 500 billion yuan ($70.25 billion) to accelerate investment projects.
The state commission will urge local authorities to speed up project starts and construction, boost effective investment, and support stable economic growth.
The funding will be used as seed capital for projects in areas including the digital economy, artificial intelligence, the low-altitude economy, consumption infrastructure, transportation and logistics.
India
India considers nuclear liability fund for major accidents, sources say
India plans to set up a nuclear liability fund to cover accident compensation in excess of 15 billion rupees ($169 million) owed by plant operators.
The move holds out potential to unlock long-stalled private and foreign investment in the nuclear industry, by aligning India’s compensation framework with global norms.
Notes:
India plans to expand nuclear power capacity 100GW by 2047.
New Zealand
New Zealand to Ease Strengthening Rules on Quake-Prone Buildings
The government is implementing clearer definitions to identify buildings that pose a genuine risk to human life in medium and high seismic zones.
This is to reduce costs and confusion for owners.
Since 2017, engineers have applied a rule that requires a structure to be at least 34% of the New Building Standard.
This has seen 8,000 properties earmarked for strengthening or demolition.
The new system will drop the 34% of NBS rule and provide specific definitions of an earthquake-prone building.
The new regime, which will require a law change, will more than halve the number of properties needing earthquake strengthening.
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan restricts money laundering through real estate
The country adopted a new law introducing two key changes to the housing construction sector:
Construction companies are prohibited from raising funds from unit owners without a guarantee from “Kazakhstan Housing Company“ JSC or permission from the local executive body.
The purchase of apartments in cash is now prohibited with funds from capital owners can be transferred to construction companies only through banks.
The law should help clean the construction market of unreliable players.
Notes:
Something that ConTech founders in certain countries (this is not a comment on Kazakhstan) need to be mindful of is the use of cash payments.
Some sectors may not want the digitization of payments having a preference for using cash.
For founders, they need to be mindful of this dynamic and understand how to navigate the competing interests from a variety of stakeholders.
While your solution may increase productivity, this may not be a requirement or ultimate aim in certain projects and regions.
National Infrastructure Projects & Priorities
US
Trump’s Team Explores Government-Backed Manufacturing Boost
Trump’s team is weighing a plan to spur the construction of factories and other infrastructure in a bid to jump-start the American manufacturing sector.
Under the plan, the administration would use money from a $550 billion investment fund established as part of trade negotiations with Japan.
This would invest in the development of semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, critical minerals, energy, ships and quantum computing.
Some of the projects would be granted preferential treatment from the government, including expedited regulatory review.
US to convert retired coal plant into 350-megawatt nuclear fusion power plant
The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) recently announced that it has issued a Letter of Intent (LOI) to the nuclear fusion company Type One Energy.
The proposal focuses on Type One Energy’s Infinity Two power plant design, a 350 megawatt-electric (350 MWe) facility intended to provide baseload power to the grid.
The companies are aiming to have the pilot fusion plant operational by the mid-2030s.
Notes:
Today’s nuclear power plants generate energy through fission, which involves splitting heavy atoms.
Fusion, the process that powers the Sun, creates energy by fusing light atoms together.
Fusion offers the potential for virtually limitless clean energy with minimal waste and improved safety compared to fission.
The technology remains in development and is not yet operational at a commercial scale.
OpenAI Unveils Plans for Seemingly Limitless Expansion of Computing Power
OpenAI laid out its vision for a vast, $1 trillion build-out of computing warehouses across the U.S. and abroad.
They envision a need for more than 20 gigawatts of computing capacity to meet the explosive demand for ChatGPT.
Each gigawatt of capacity is expected to cost roughly $50 billion.
Related:
PG&E Will Upgrade Infrastructure as Part of 5-Year, $73-Billion Investment Plan
California utility PG&E announced a $73-billion capital expenditure.
PG&E serves about 5.3-million electricity customers, along with 4.6-million customers for natural gas, in 47 of California’s 58 counties.
They filed a plan in March for the 2026-28 period to build 700 miles of underground power lines, and complete 500 miles of additional wildfire safety system upgrades.
They also said their grid modernization efforts would include developing and deploying distribution planning tools for grid management.
Notes:
Grid Tech continues to remain a major opportunity
India
India plans mega-dam to counter China water fears
India says the proposed new structure could counteract China’s building of a dam upstream in Tibet.
This would stockpile water and guard against releases of weaponised torrents.
Qatar
Korean construction company lands contract for Qatar’s largest-ever solar project
Construction company Samsung C&T E&C (engineering and construction group) has won Qatar’s largest solar power project.
The 2,000MW facility is worth US$1 billion.
It involves 2.74 million solar panels on a 27 sq km site in Dukhan and will supply electricity to 750,000 households by 2030.
Africa
China Signs $1.4 Billion Mao-Era African-Rail Revamp Deal
China signed a deal with Zambia and Tanzania for the revitalization of the Tanzania-Zambia railway.
The revamp of the line will cost about $1.4 billion and will take two years to complete, quadrupling the line’s capacity to about 2 million tons yearly.
The line will compete with another that the US and EU are backing and connects the same copper-rich region to an Atlantic port on Africa’s west coast.
The investments highlight intensifying global competition for access to Africa’s critical minerals
News
2026’s top construction conferences
How Wall Street’s Big Bets on A.I. Are Driving Interest in Huge Parking Lots
Inside the Nuclear Bunkers, Mines, and Mountains Being Retrofitted as Data Centers
Infra.Market Files Confidential IPO Papers With SEBI
The company is looking to raise around INR 5,000 Cr ($563.3 Mn) via the IPO.
An $800 Billion Revenue Shortfall Threatens AI Future, Bain Says
By 2030, AI companies will need $2 trillion in combined annual revenue to fund the computing power needed to meet projected demand.
Their revenue is likely to fall $800 billion short of that mark.
It’s predicted monetization of services like ChatGPT trail the spending requirements for data centers and related infrastructure.
US to See $350 Billion Nuclear Boom to Power AI, Report Says
What is infrastructure? (McKinsey)
Triangles, Crescents, Slivers: Can Odd-Shaped Lots Help Ease the Housing Crisis?
As needs escalate, more U.S. cities and states are making it easier to build on irregular and long-overlooked lots.
AI Data Centers Are Sending Power Bills Soaring
If I missed anything this week, please reply and let me know! I’ll make sure to include it next week.